New FDA Clearance Illustrates the Utility of the i:X to Reliably Detect Clinically Significant Bacteria that Impedes Wound Healing
TORONTO, CANADA – (June 29, 2022) MolecuLight Inc., the leader in point-of-care fluorescence imaging for real-time detection of wounds containing elevated bacterial loads, announces that it has received an expansion to its FDA 510(k) clearance for the MolecuLight i:X® imaging device’s ability to detect the location of elevated bacterial loads (>104 CFU/g) in wounds. The expanded labelling also includes the device’s ability to identify areas of wounds containing more bacterial species, including key target pathogens of interest to the CDC that are major causes of antimicrobial resistance1. Detectable species include gram-negative and gram-positive species, aerobes and anaerobes. This expanded labeling is based on a detailed retrospective statistical analysis of over 350 patients.
“We are thrilled with the FDA’s new clearance for MolecuLight’ ability to determine the location of elevated bacterial loads in wounds, in addition to the ability to identify regions with more bacterial species of interest”, says Anil Amlani, MolecuLight’s CEO. “Clinicians worldwide are using the MolecuLight device to visualize regions with clinically significant bacterial loads and more species of concern. With point-of-care information on bacterial load and its locations through use of a MolecuLight device, clinicians can act immediately to tailor their cleaning, debridement, antimicrobial strategies and treatments accordingly.”
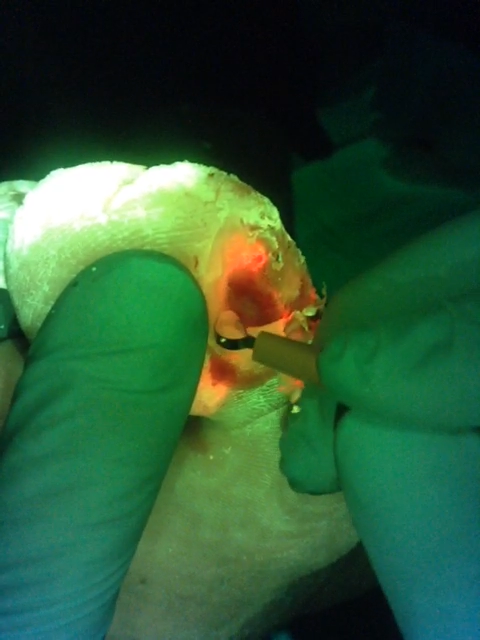
This video (courtesy of Rose Raizman) illustrates the importance of visualizing the location of elevated bacterial load in a wound. In this scenario, the clinician is using MolecuLight i:X to inform their decision-making and target their wound hygiene to the areas of red fluorescence. Regions of red, indicating that the wound contains clinically significant (>104 CFU/g) levels of bacterial burden, are clearly visible on the patient’s diabetic foot ulcer (see image).
In addition, the FDA has also recognized MolecuLight’s ability to visualize regions containing troublesome bacterial species at the point-of-care. The MolecuLight device can be used to enable fluorescence-guided tissue biopsies to these regions to detect a higher number of pathogens of interest (defined by the CDC as increasing risk to develop antibiotic resistance) compared to standard-of-care-guided biopsies. The CDC has identified antibiotic resistance as “one of the greatest global public health challenges of our time”1. Strategies to combat antibiotic resistance include containing emerging threats through early detection and aggressive response and improving appropriate antibiotic use through antimicrobial stewardship programs. The expanded use of diagnostic tools, like MolecuLight, to improve accuracy and speed of pathogen detection has been called out to help improve appropriate antibiotic selection and reduce unnecessary antibiotic use1.
MolecuLight was the first to receive FDA de novo clearance for its MolecuLight i:X imaging platform and has subsequently received three additional FDA 510(k) clearances for the device.
1 CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2019. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC;2019